Assignment-1 BPOPS103
1 Write a C Program for the following
1.1 Sum of 2 numbers
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int num1, num2;
printf("Enter two numbers: ");
scanf("%d %d", &num1, &num2);
printf("The sum of %d and %d is %d\n", num1, num2,num1+num2);
return 0;
}
1.2 Area and perimeter of a circle
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int rad;
printf("Enter the radius: ");
scanf("%d", &rad);
printf("Area: %0.2f\n", 3.14*rad*rad );
printf("Perimter: %0.2f", 2*3.14*rad );
return 0;
}
1.3 Area and perimeter [2*(l+b)] of a rectangle
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
float l,b;
printf("Enter L and B: ");
scanf("%f %f", &l, &b);
printf("Area: %0.2f\n", l*b );
printf("Perimeter: %0.2f", 2*(l*b) );
return 0;
}
1.4 Calculation of simple interest : ptr/100
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
float p,t,r;
printf("Enter P, T and R: ");
scanf("%f%f%f", &p, &t,&r);
printf("SI= %0.2f\n", (p*t*r)/100 );
return 0;
}
1.5 Convert temperature in degree to Fahrenheit
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
float c;
printf("Enter the celsius: ");
scanf("%f", &c);
printf("Fahrenheit: %0.2f\n",c*9/5+32);
return 0;
}
1.6 Convert temperature in degree to Fahrenheit
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
float c;
printf("Enter the celsius: ");
scanf("%f", &c);
printf("Fahrenheit: %0.2f\n",c*9/5+32);
return 0;
}
1.7 Greatest of 2 numbers
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int a,b;
printf("Enter Two Number: ");
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
if(a>b){
printf("%d is Greater",a);
}
else{
printf("%d is Greater",b);
}
return 0;
}
1.8 To check a number is odd or even
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int a;
printf("Enter the Number: ");
scanf("%d",&a);
if(a%2==0){
printf("%d is Even",a);
}
else{
printf("%d is Odd",a);
}
return 0;
}
1.9 Greatest of 3 numbers
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int a,b,c;
printf("Enter Two Number: ");
scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c);
if(a>b && a>c){
printf("%d is Greatest",a);
}
else if(b>c) {
printf("%d is Greatest",b);
}
else{
printf("%d is Greatest",c);
}
return 0;
}
1.10 Sum of n natural numbers
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int n, sum = 0;
printf("Enter a positive integer: ");
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
sum += i;
}
printf("The sum of the first %d natural numbers is %d\n", n, sum);
return 0;
}
2 Which of the following are valid variable names in C?
1999_space_appleiNtELone_2for#12i.b.mhelp+me
Answer:
1999_space- Invalid (starts with a digit)_apple- ValidiNtEL- Validone_2- Validfor- Invalid (reserved keyword in C)#12- Invalid (contains a special character)i.b.m- Invalid (contains periods, which are not allowed)help+me- Invalid (contains a plus sign, which is not allowed)
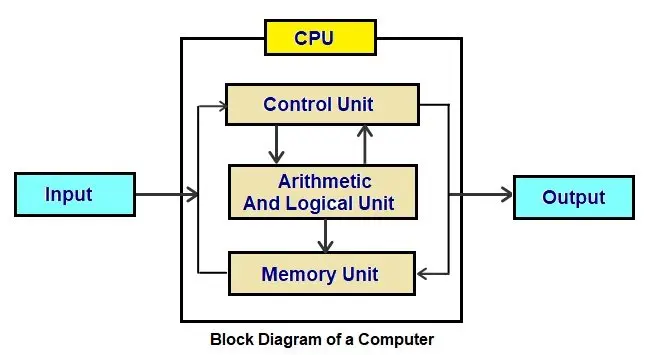
3 Explain the functional block diagram of a computer.
- Input unit: The input unit is responsible for receiving data and instructions from the user. Examples of input devices include the keyboard, mouse, and scanner.
- Output unit: The output unit is responsible for displaying the results of the computer’s processing to the user. Examples of output devices include the monitor, printer, and speakers.
- Central processing unit (CPU): The CPU is the brain of the computer. It is responsible for executing instructions and processing data. The CPU consists of two main components: the arithmetic logic unit (ALU) and the control unit.
- Memory unit: The memory unit is responsible for storing data and instructions that are being processed by the CPU. There are two main types of memory: main memory and secondary storage. Main memory is volatile, meaning that the data stored in it is lost when the computer is turned off. Secondary storage is non-volatile, meaning that the data stored in it is retained even when the computer is turned off. Examples of secondary storage devices include hard drives, solid state drives, and optical discs.